
Facial Masculinization Surgery Los Angeles – FMS LA
Facial masculinization surgery (FMS) describes a set of procedures used to masculinize the face. These are performed for transgender men, cisgender men, and gender non-binary and non-conforming individuals. The procedures include the ones listed below:
Forehead augmentation (increase in forward protrusion of the brow)
Rhinoplasty (to augment or lengthen the nose)
Jaw augmentation
Genioplasty (chin surgery)
These procedures can be performed in isolation or they can be combined during one or more operations.
Facial Differences Between Men and Women
Many facial features differ between cisgender men and women. These are usually taken from population averages and do not describe an individual person. Some features may be more or less prominent in individual cisgender men or women and there can be significant variations within genders. The features also vary significantly between individuals with different ethnic backgrounds. The features that can be addressed during facial masculinization surgery are the forehead, nose, jaw, and Adam’s apple. Additional details are listed below.


Forehead
Cisgender men generally have a higher hairline with a different shape than cisgender women.1 Male hairlines tend to be M-shaped and female hairlines tend to be rounded. Cisgender men commonly have more prominent brow bossing.2




Nose
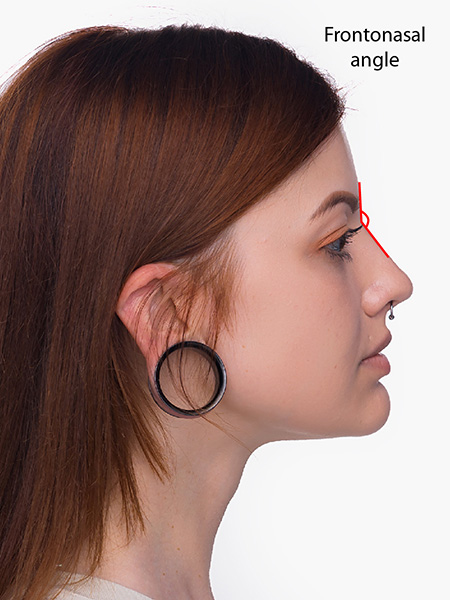
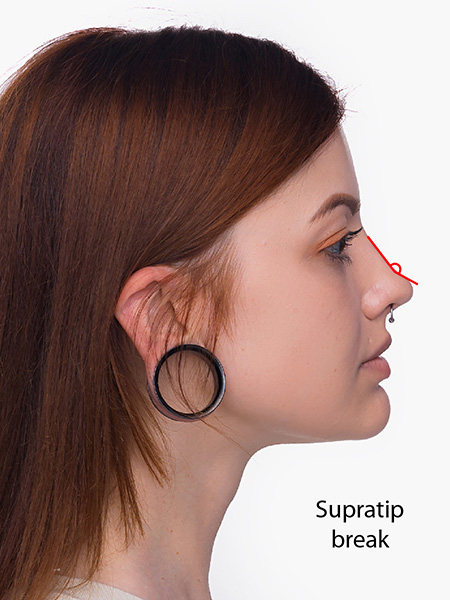
Cisgender men generally have a more acute nasolabial angle than cisgender women.3 The nasolabial angle is the angle between the upper lip and the lower part of the nose. Men generally prefer less of a supratip break than women.4 A supratip break is the small indentation immediate above the tip of the nose.





Mandible (Jaw)
Cisgender men generally have larger mandibles (lower jaw).5 This includes the height at the back of the jaw, the height at the front of the jaw, the width at the back of the jaw, and the width of the chin.6, 7
Thyroid Cartilage (Adam’s Apple)
Cisgender men generally have more thyroid cartilages (Adam’s apples) that are more prominently angulated than cisgender women.8, 9



Dr. Mittermiller is a specialty trained plastic surgeon who primarily operates in the Los Angeles area. He is passionate about craniofacial surgery, gender-affirming surgery, and rhinoplasty.
Click here to learn more about Dr . Mittermiller
or
Contact us today to schedule a consultation.
Surgical procedures for FMS
Forehead Augmentation

Women commonly have a softer brow with a smoother transition from the forehead to the eyes. Augmentation of the forehead produces a stronger, more masculine brow for forehead masculinization.
Augmentation of the forehead is most commonly performed with a forehead implant. Off-the-shelf implants can be used for forehead augmentation, but the shape is frequently not perfectly aligned with the natural, native shape of the patient’s brow. A custom implant provides improved contouring of the implant for ideal placement. Custom implants can be made from silicone, polyetheretherketone (aka PEEK)10, and porous polyethylene.
Alternatively, it can be augmented with bone cement or bone grafts. Bone cement has the benefit of lower cost compared to a custom implant. However, this requires sculpting of a brow prominence during the operation and is not as precise as a machine-manufactured implant. Bone grafting requires harvest of the bone, which results in potential complications from the donor sites and it also has the difficulty of sculpting a natural-appearing brow bone in the operating room.
Least commonly, it can be augmented with fat grafting or fillers. This is described in greater detail in the non-surgical section of this article.
Rhinoplasty

Men commonly have straighter, larger noses than women. A masculinizing rhinoplasty can create a stronger nose that does not compromise breathing. A rhinoplasty can be performed to create a straighter nose when seen in profile and rotate the nose as seen in profile to decrease the nasolabial angle. More details about rhinoplasty can be found here: Rhinoplasty
A rhinoplasty can be performed to make the nose appear more masculine while also correcting any aesthetic imperfections or to better match the aesthetic preferences of the individual
A masculinizing rhinoplasty frequently requires the use of cartilage grafts for augmentation. There are a variety of grafts that can be used during rhinoplasty and these are described in greater detail here: Cartilage Grafts in Rhinoplasty
Rhinoplasty frequently requires placing a small incision on the undersurface of the nose and within the nose. Through these small incisions, major modifications of the nose structure can be performed. The incisions in these locations usually heal very well and are difficult for other people to see at a conversational distance.
Jaw Augmentation

Jaw masculinization frequently involves the use of implants to strengthen the angularity and chiseled appearance of the face. Implants come in a variety of shapes and sizes. There are a variety of different methods for choosing and designing implants for the chin and jaw. This can involve using implants that have previously been designed or creating custom implants. The custom implants can be created based on individualized measurements or comparing to the skull of a cisgender man.11 It is important to discuss the options with a qualified surgeon who has experience with the placement of facial implants.
Chin implants can be placed to increase the height, width, or projection of the chin. They can also be used to change the shape of the chin. Masculinization of the chin commonly involves creating a more square-shaped chin.
Jaw angle implants are placed at the back corners of the jaw to create a more chiseled, defined jaw angle. Jaw angle implants are used to increase the height or width of the jaw towards the back.
Wrap-around jaw implants are custom implants that add volume to and change the shape of the entire jaw from front to back. These implants are the gold-standard for individually tailoring the shape of the jaw across the entire face.
Custom Wrap-Around Implants

A custom wraparound jaw implant is a valuable tool in facial masculinization surgery, particularly for individuals seeking a more pronounced and angular jawline. This specialized implant is used when the patient desires a broader and more defined jaw that is characteristic of a masculine facial structure. It is an ideal option for those with a naturally narrow jawline or for individuals who have undergone hormone therapy but have not achieved the desired level of masculinization in their jaw area.
The custom wraparound jaw implant is carefully designed to match the patient’s unique facial proportions and desired aesthetic outcome. It is crafted to envelop the entire jawbone, providing a seamless and natural enhancement to the jawline. The implant is precisely tailored to fit snugly around the jawbone, creating a harmonious integration with the existing facial features.
This type of implant is particularly effective in achieving a more masculine facial contour. By enhancing the width and projection of the jawline, the custom wraparound jaw implant helps create a stronger and more angular appearance. It contributes to the overall balance and symmetry of the face, aligning with the patient’s gender identity.
A custom wraparound jaw implant is an excellent option for individuals seeking a more pronounced and angular jawline in facial masculinization surgery. It is used to address a naturally narrow jawline or to enhance the effects of hormone therapy. By carefully designing and fitting the implant to the patient’s unique facial structure, it provides a seamless and natural enhancement, helping individuals achieve their desired masculine facial features.
Genioplasty (Chin Surgery)
Masculinizing chin surgery is performed to strengthen the lower face and jaw. This can be performed with implants or by repositioning the bone of the chin. Repositioning of the chin bone requires performing a cut into the bone of the chin, moving the chin segment(s), and securing it/them into a new position. Frequently, masculinizing jaw surgery is best performed with augmentation in multiple areas of the jaw and this is frequently performed through the use of implants as previously described.
Adam’s Apple Augmentation
Augmentation of the Adam’s apple is commonly performed through an incision on the neck or underneath the chin. Cartilage is then shaped into the desired form and secured to the existing thyroid cartilage.
Illustrations and Simulations
Facial masculinization surgery usually consists of augmenting the facial skeleton with implants. The implants can be off-the-shelf or customized to the individual. Facial implants to masculinize the face are most effective when placed at the brow, mandibular angles, and chin.




Non-Surgical Interventions for FMS
Hormone Therapies
Oftentimes, transgender men will start their medical and physical transition with hormonal therapies. Hormonal treatments have been shown to decrease the amount of cheek tissue and increase jaw tissues. 12 Testosterone has also been shown to result in an increase in facial hair and male-pattern hair loss. 13 Too much hair loss may not be preferable for some individuals but for others with a modest effect, it can further serve to masculinize the face.
Hairline Masculinization
As mentioned above, hairline masculinization often occurs with hormone therapy. However, this is rarely a highly desired component of facial masculinization. It has been reported that epilation techniques can be considered, such as laser hair removal or electrolysis, but that this intervention is rarely sought after. 14
Non-Surgical Forehead Augmentation
Creation of additional brow prominence has been described with the use of volumetric fillers, but this is a procedure not commonly performed. 15 Injection of filler often provides only a temporary modification and it is often not possible to obtain a variation of enhancement in different parts of the forehead that would appear natural for a cisgender man. One must also consider the fact that filler is soft whereas natural brow prominences are hard due to the underlying bony structure. Fat grafting may provide a more permanent increase in brow projection, but there is frequently a high degree of fat reabsorption after injection and it still does not provide for a firm structural framework of the brow.
Eyebrow Masculinization
Eyebrow masculinization has been described, but it is not commonly performed. 16 Non-surgical eyebrow masculinization can theoretically be performed with botulinum toxin (e.g. Botox) or with hair transplantation to the brows. Botulinum toxin can theoretically be used in the frontalis muscle to decrease the upward pull on the brows and cause them to drop into a more masculine position. Hair transplantation can theoretically be performed by harvesting hair and transplanting it to the eyebrows. One problem that could occur from this technique is that the hair would grow to the length of where it is transplanted from. If transplanted from the top of the head, the hairs would require frequent trimming to keep them at a normal eyebrow hair length.
Non-Surgical Rhinoplasty
A non-surgical rhinoplasty describes a procedure where filler is injected into the nose to modify its shape. Since men commonly have a larger nose with a straighter bridge when viewed from profile, filler can be injected into the bridge of the nose for masculinization. Non-surgical rhinoplasty procedures have the downsides of providing a temporary result. Filler frequently dissolves within 1-2 years and requires re-injection to maintain the same result.
Non-Surgical Jaw Augmentation
Jaw augmentation can be performed with the use of fillers. This provides a quick, relatively inexpensive way to add additional volume to the jaw. The downsides of filler injections are similar to those seen on other parts of the face. The filler is frequently temporary and requires multiple injection sessions over time. A large volume of filler is frequently required in order to produce a significant effect. It may be less expensive for small temporary augmentations, but overtime, it often becomes more economical to undergo surgical augmentation of the jaw with implants.
Frequently Asked Questions
Considerations
How can I make my face look more masculine without surgery?
There are multiple nonsurgical methods for making the face appear more masculine.
Facial hair: Growing a beard or mustache can help create a more masculine appearance. You should experiment with different styles and lengths to find what suits you best.
Hairstyle: You can choose to go for a shorter haircut or a style that accentuates your facial structure. It may be helpful to consult with a professional hairstylist who can recommend a cut and style that complements your face shape and desired look.
Contouring and highlighting: Makeup techniques can be used to create the illusion of a more chiseled jawline, prominent cheekbones, and a stronger brow. You can research contouring and highlighting tutorials to learn how to use makeup effectively.
Strength training and facial exercises: Building muscle in the neck and jawline area can contribute to a more defined and masculine appearance. Incorporate exercises such as jaw clenching and neck curls into your workout routine.
Posture: Maintaining good posture can make a significant difference in how your face appears. Stand tall, keep your shoulders back, and hold your head up high. This can give you a confident and masculine look.
Style choices: Consider adopting a style that aligns with your desired masculine image. Clothing, accessories, and grooming choices can all play a part in enhancing your overall appearance.
Remember, beauty and attractiveness are subjective, and the most important thing is to feel comfortable and confident in your own skin. Embrace your unique features and express yourself in a way that makes you happy.
How can I make my face more masculine with surgery?
If you are considering surgical options to enhance masculine features in your face, it is essential to consult with a qualified and experienced surgeon who can assess your individual needs and provide personalized recommendations. To reiterate the items above, here are some common surgical procedures that can potentially help achieve a more masculine facial appearance:
Facial implants: Implants can be used to enhance specific areas of the face, such as the jawline, chin, or cheeks. They can add definition and create a more masculine structure.
Rhinoplasty: Nose surgery, or rhinoplasty, can alter the shape and size of the nose to create a more masculine profile. This procedure can involve reshaping the nasal bridge, refining the tip, or changing the overall size of the nose.
Jawline surgery: Procedures like jaw augmentation or jawline contouring can enhance the definition of the jaw and chin. They involve reshaping or augmenting the bone structure to create a stronger and more masculine appearance.
Adam’s apple enhancement: In some cases, individuals may desire a more prominent Adam’s apple. This can be achieved through a procedure called Adam’s apple enhancement or thyroid cartilage enhancement.
Liposuction or facial fat grafting: These procedures involve removing excess fat from certain areas of the face or adding fat to others to create a more sculpted and masculine facial contour.
It is crucial to have a thorough consultation with a surgeon trained in gender-affirming facial surgery to discuss your goals, understand the potential risks and benefits, and explore the most suitable surgical options for your specific situation. Surgery is a personal decision, and it is important to have realistic expectations and understand the potential limitations of each procedure.
Surgery
How much does facial masculinization surgery cost?
The cost of facial masculinization can be extremely variable. The costs depend on multiple factors, which are listed below.
– Whether insurance is covering all or part of the operation
– The number and types of procedures being performed during the operation
– The duration of the operation
– Variations in pricing between individual surgeons
The best way to get an estimate for the cost of facial masculinization surgery is to contact a gender-affirming facial surgeon to discuss your specific situation.
Click here to contact the office of Dr. Mittermiller.
How do I prepare for surgery?
The first step is to have a consultation with a surgeon who specializes in gender-affirming facial surgery. They will discuss the facial features concerning to you and may suggest additional procedures.
A CT scan may be performed to evaluate the bones of the face. This allows the patient and surgeon to better visualize the underlying bone structure of the face to best tailor a surgical treatment.
If the surgery is being performed for gender dysphoria, letters from one or more health providers may be necessary to state the need for facial masculinization to help relieve symptoms of gender dysphoria.
During the workup, you will commonly be asked about your medical history. This includes any medical problems that may exist, whether you have previously had surgery, what medications you take, which allergies you have, and whether you have any habits such as smoking or drinking.
How is the recovery from facial masculinization surgery (FMS)?
Recovery from facial feminization surgery is based on the number and types of procedures that are performed during the operation.
In general, recovery from facial masculinization surgery is much easier and less painful than recovery from facial feminization surgery.
The recovery is easiest with fewer procedures. It becomes progressively more difficult as additional procedures are added. The recovery becomes more involved when larger procedures are performed, such as an osseous genioplasty (chin surgery without implant). It is best to look at each individual procedure to see how the recovery will be after that procedure.
Many of the effects from facial masculinization surgery will be seen immediately after surgery. There will be swelling and bruising after the operation that can last for a few weeks. There is subsequently minor residual swelling of the face that can persist for over a year.
How painful is the recovery from FMS?
The amount of pain is dependent on the procedures that are performed. Patients commonly describe osseous genioplasty (cuts in the bone to reshape the chin) to be one of the more painful procedures. You will receive pain medications following the procedure to make you comfortable.
How much time do I need to take off work after facial masculinization surgery?
For many surgeries, taking at least one week off work is ideal. This allows the swelling to subside and for the incisions to become less noticeable. However, depending on the extent of surgery and the desire for privacy, some people opt to take a few weeks off work to allow the incisions to heal more completely and for the swelling to subside more significantly.
What are the risks of FMS?
The risks of facial masculinization surgery are related to the individual procedures themselves. In general, facial masculinization consists of augmenting the facial skeleton. With the augmentation procedures, there can be a risk of infection or nerve damage.
How long will the results last from facial masculinization surgery?
The procedures performed for facial masculinization surgery will produce results that are permanent. Your body will continue to age though. Aging will result in standard changes, but the facial structures will be permanently different than they were before the operation.
Am I a candidate for facial masculinization surgery?
It is important to discuss facial masculinization surgery with your surgeon to determine your candidacy. There are a multitude facial features that can be addressed to varying degrees. Individual preferences often play a major role in determining which components of facial masculinization surgery are right for you.
Can cisgender men get facial masculinization surgery?
Yes! See link here.
How do I find the best facial masculinization surgeon near me in Los Angeles, California?
You should continue to research facial masculinization surgery and try to determine which surgeons offer FMS as part of their practice. Finding the best facial masculinization surgeon may require talking with friends and physicians to share suggestions. You want a surgeon who has the appropriate training for facial masculinization surgery and who is dedicated to their patients.
Dr. Mittermiller is a fellowship-trained craniofacial surgeon with experience in facial masculinization surgery. He can be seen at the practice’s office in Los Angeles.

Dr. Mittermiller is a plastic surgeon with specialty training in craniofacial surgery and facial feminization surgery. He is primarily located in Los Angeles, California and serves the broader Southern California area.
Contact us today to schedule a consultation.
Citations
- Rodman R, Sturm AK (2018) Hairline Restoration: Difference in Men and Woman-Length and Shape. Facial Plast Surg 34 (2):155-158. doi:10.1055/s-0038-1636905
- Douglas Ousterhout MD (1987) Feminization of the forehead: contour changing to improve female aesthetics. Plast Reconstr Surg 79 (5):701-713. doi:10.1097/00006534-198705000-00003. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3575517/
- de Freitas DS, de Freitas MR, Janson G, de Freitas KM, Cardoso CL (2014) Nasolabial angle at rest and upon smiling. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 72 (12):2567 e2561-2565. doi:10.1016/j.joms.2014.07.034
- Barone M, Cogliandro A, Salzillo R, List E, Panasiti V, Tenna S, Persichetti P (2019) Definition of “Gender Angle” in Caucasian Population. Aesthetic Plast Surg 43 (4):1014-1020. doi:10.1007/s00266-019-01366-w
- Direk F, Uysal, II, Kivrak AS, Unver Dogan N, Fazliogullari Z, Karabulut AK (2018) Reevaluation of Mandibular Morphometry According to Age, Gender, and Side. J Craniofac Surg 29 (4):1054-1059. doi:10.1097/SCS.0000000000004293
- Direk F, Uysal, II, Kivrak AS, Unver Dogan N, Fazliogullari Z, Karabulut AK (2018) Reevaluation of Mandibular Morphometry According to Age, Gender, and Side. J Craniofac Surg 29 (4):1054-1059. doi:10.1097/SCS.0000000000004293
- Siddapur KR (2016) Gender Identification Study of a Dry Human Mandible by Assessing its Measurable Dimensions. Indian Journal of Forensic Medicine & Toxicology 10 (1):89-93. doi:10.5958/0973-9130.2016.00020.7
- Sagiv D, Eyal A, Mansour J, Nakache G, Wolf M, Primov-Fever A (2016) Novel Anatomic Characteristics of the Laryngeal Framework: A Computed Tomography Evaluation. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 154 (4):674-678. doi:10.1177/0194599815627781
- Glikson E, Sagiv D, Eyal A, Wolf M, Primov-Fever A (2017) The anatomical evolution of the thyroid cartilage from childhood to adulthood: A computed tomography evaluation. Laryngoscope 127 (10):E354-E358. doi:10.1002/lary.26644
- van der Wel H, Merema BJ, Kraeima J, Schepers RH, Jansma J (2024) Facial Masculinization Surgery Using Polyetheretherketone Alloplasty: Statistical Shape Modeling–based Implant Designs. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery – Global Open 12 (7):e6012. doi:10.1097/gox.0000000000006012 https://journals.lww.com/prsgo/fulltext/2024/07000/facial_masculinization_surgery_using.75.aspx
- Moghadam S, LaGuardia JS, Chin MG, Huang KX, Bedar M, Justine Lee (2024) Virtual Modeling in Gender-Affirming Facial Masculinization Surgery. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery 154 (6):1229e-1232e. doi:10.1097/PRS.0000000000011336 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39591366/
- Tebbens M, Nota NM, Liberton N, Meijer BA, Kreukels BPC, Forouzanfar T, Verdaasdonk RM, den Heijer M (2019) Gender-Affirming Hormone Treatment Induces Facial Feminization in Transwomen and Masculinization in Transmen: Quantification by 3D Scanning and Patient-Reported Outcome Measures. J Sex Med 16 (5):746-754. doi:10.1016/j.jsxm.2019.02.011 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30926514/
- Hembree WC, Cohen-Kettenis P, Delemarre-van de Waal HA, Gooren LJ, Meyer WJ, 3rd, Spack NP, Tangpricha V, Montori VM, Endocrine S (2009) Endocrine treatment of transsexual persons: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 94 (9):3132-3154. doi:10.1210/jc.2009-0345 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19509099/
- Akhavan AA, John Pang MD, Shane Morrison MD, Thomas Satterwhite MD (2024) Gender Affirming Facial Surgery-Anatomy and Procedures for Facial Masculinization. Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am. doi:10.1016/j.coms.2024.01.001 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38458858/
- Scherer MA (2016) Specific aspects of a combined approach to male face correction: botulinum toxin A and volumetric fillers. J Cosmet Dermatol 15 (4):566-574. doi:10.1111/jocd.12247
- Akhavan AA, John Pang MD, Shane Morrison MD, Thomas Satterwhite MD (2024) Gender Affirming Facial Surgery-Anatomy and Procedures for Facial Masculinization. Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am. doi:10.1016/j.coms.2024.01.001 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38458858/